Getting started in Affiliate Marketing? Feeling a little lost in the sea of acronyms and other technical jargon flooding you from all sides? Look no further: we’ve got you covered with this in-depth glossary. Find out not only the most popular affiliate terminology, but all the terms and expressions every Affiliate Marketer ought to know.
But first, what is Affiliate Marketing?
In its simplest terms, Affiliate Marketing is a type of performance-based marketing, which means that you, as an Affiliate, get paid when a visitor completes a desired action, whether that’s registering on a website, filling out a form, or purchasing a product. That’s what’s called a conversion - where you convert an action into revenue.
Basically, picture it as door-to-door salesmen representing a brand and trying to sell their products for a share of the profit. Pretty simple, uh?
Desired goals or actions may vary from offer to offer (offers are what you, as an affiliate, show your audience), but the most common one is to convert a web visitor into a paying customer.
And who pays you for that conversion, exactly? That would be the provider of an offer, also known as “the sponsor” or “the advertiser”. Basically, it’s a company that has something to sell and needs someone to promote it. And that’s where you come in!
Sponsors typically deal with affiliates through an affiliation program which allows would-be affiliates to advertise their offers for a commission (or payout) in return.
This commission can be earned through 4 different methods:
Pay-Per-Click (PPC), where you, as an affiliate, send your traffic to the seller’s website and earn a certain amount of commission each time this happens, whether a sale occurs or not.
Pay-Per-Lead (PPL), where you direct your traffic to the seller’s website and invite them to fill out a contact form, providing the seller with some of their personal information. This converts your traffic into “leads”, and affiliates earn a commission for each lead generated. In some cases, your traffic may also fill out the form directly on your platform.
Pay-Per-Sale (PPS), which is pretty self-explanatory: you earn a certain amount of money from the advertiser for each sale completed by your traffic.
And finally Revshare, in which advertisers share (that’s right!) a predefined percentage of their product or service price with affiliates when they complete a sale.
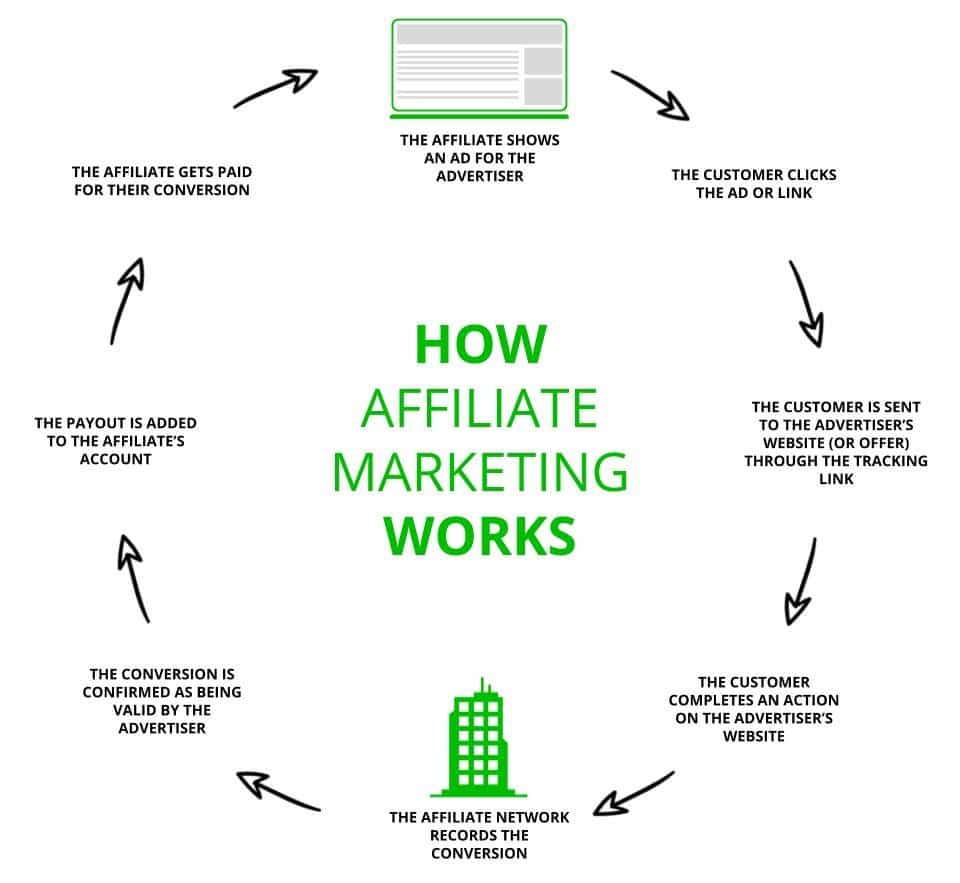
Need a more visual representation of the cycle?
Here’s exactly how Affiliate Marketing works:
Contents
- A/B Testing (Split testing)
- Above the Fold
- Ad Tools
- Ad Network
- Advertiser
- Affiliate
- Affiliate Agreement
- Affiliate Link
- Affiliate Manager
- Affiliate Program
- Affiliate Software
- Affiliate Tracking (Tracking URL)
- API
- Backlink
- Banner Ad
- Bid
- Billing
- Black Hat SEO
- Browser
- Capping
- Chargeback
- Cloaking
- Co-branding
- Commission
- Contextual Advertising
- Conversion Rate
- Cookie
- CPA / RPA
- CPC
- CPI
- CPM / RPM
- Creative
- CTR
- Deep linking
- Direct Linking / Direct to Form
- Domain
- Double Opt-In (DOI)
- eCPM
- EPC
- Flat rate
- Geo-targeting
- Global Postbacks
- Gross Click
- Impression
- In-house
- Landing page
- Lead Scrubbing
- Media Buying
- Merchant
- Multi-CPA
- Multiple Tiers
- Niche
- Offer
- Pay-Per-Lead (PPL)
- Pay-Per-Sale (PPS)
- Performance-Based Marketing
- Postback
- PPC / RPC
- Prelander
- Revshare, RPS, and RS
- ROI
- RON
- Search Robots
- Segment
- SEO
- SERP
- Single Opt-in (SOI)
- Smartlink
- Spot
- Targeting
- Tracker (Sub ID)
- Unique
- Vertical
- White Hat SEO
- White Label
A/B testing
A/B testing (sometimes called split testing) is comparing two versions of a promotional tool to see which one performs better.
Example:
You compare two web pages by showing the two variants (let’s call them A and B) to similar visitors at the same time. The one that gets a better conversion rate, wins.
Read more:
- A/B Testing: The Method That Works
- The Complete Guide to A/B Testing
- Why You Should Spend More Time A/B Testing Your Ads
Above the Fold
Above the Fold content – also known as Above the Scroll in web design – refers to an area of the webpage shown without the need of scrolling down. This spot is extremely important to take into consideration for online marketers since it is the very first thing readers see.
The Above the Fold area is not static and will be adjusted according to the different screen resolutions used by the viewers and the number of pixels displayed by their monitors.
Activation
Initiating a sale through a new user involves an affiliate sharing a link. When someone clicks, then signs up as a user and makes their first sale, it is considered activation.
Ad Tools
The ad tools are comprised of all the web advertising elements included in your funnel.
Therefore, ad tools can include multiple types of material such as banners, landing pages, pre-rolls, iframes, etc.
Ad Exchange
Groups of traffic sources linked to DSPs (Demand-Side Platforms) and SSPs (Supply-Side Platforms).
Ad Network
Ad Networks are like the Wall Street of Web Street. Ad Networks connect buyers to sellers. And since they deal with high volumes of traffic, they have a better knowledge of the price market.
This is where you go to access a diverse array of traffic sources.
But their huge advantage is that they make Media Buying easier and they offer a wide variety of support.
In adult, the five main Ad Networks are TrafficJunky, ExoClick, TrafficFactory, Grand Slam Media and Media Reps.
Adware
Commonly known as "spyware," it often comes bundled with downloaded programs, catching users unaware. These ads are typically unwelcome and challenging to remove, even after uninstalling the associated program
Advertiser
An Advertiser, also known as a Merchant, pays affiliates to promote various products or offers. An Advertiser owns or at least controls the advertised products or offers.
Affiliate
An Affiliate is the owner of a website, social account or mailing list who earns a commission for each click, referral or sale on a merchant’s website.
In other words, an Affiliate receives commissions based on its performance as a web marketer.
Affiliate Agreement
An Affiliate Agreement refers to the terms of service between an advertiser or a CPA Network and an affiliate.
The Affiliate Agreement outlines all responsibilities for the parties involved, including payout terms and commissions earned.
Affiliate Link
In online marketing, an Affiliate Link is a unique URL that contains the affiliate’s ID or username. Advertisers can track all traffic sent to their website by the affiliate as part of the affiliate program.
Affiliate Network
A network linking affiliates and advertisers, offering diverse tracking tech, reporting tools, and payment processing services.
Affiliate Manager
The Affiliate Manager offers dedicated help to the affiliates which, in return, drive more conversions through the affiliate program.
The primary goal of each affiliate manager is to help their affiliates MAKE MORE MONEY.
Affiliate Marketing
Online advertisers and publishers engage in revenue sharing. Compensation is tied to performance metrics like sales, clicks, or registrations. In simple terms, you earn a commission whenever your referral generates a sale by promoting others' products or services.
Affiliate Marketing Forum
A virtual community offering users access to information on diverse topics within the affiliate marketing industry.
Affiliate Program
An Affiliate Program is set up by the advertiser or merchant to promote a product or offer using a network of partners known as affiliates.
Affiliate Software
Affiliate Software is used to manage an affiliate program by providing tools such as tracking and reporting.
Generally speaking, it’s an all-in-one solution used for the management of links, affiliates, sales, leads and more.
Affiliate Tracking (Tracking URL)
Affiliate Tracking is the process of managing and tracking actions from the seller such as clicks, sales and conversions.
For advertisers or merchants, Affiliate Tracking has many uses as it can be used to measure the performance of affiliates in the network by using their unique link (ID).
Anchor Text
The characters and words in hyperlinks that are clickable and visible when linking to another web location. Beneficial for users and search engines, the link label indicates what users will encounter upon clicking, and search engines use anchor text for indexing and ranking web pages.
API
API stands for Application Programming Interface.
It’s basically a communication protocol between different servers. It allows these programs to receive and send information requests and responses to each other.
APK Offers
APK, short for Android Application Package, is the file format employed by Android operating systems for installing mobile applications, commonly known as apps.
Auto-Download Offers
After the user clicks the banner, the content is downloaded automatically without the end user's consent.
ASVOD
ASVOD, or Ad-Supported Video on Demand, refers to streaming services offering content for free, supported by advertising revenue.
Backlink
A backlink is a direct link from another website that links back to your website and drives traffic to it.
Mainly used with SEO in mind, backlinks sends a good signal to search engines which helps you rank higher in SERP.
Read this article for more information about backlinks: The path to a great link building strategy.
Banner Ad
A Banner Ad is the embedding of an advertisement to be displayed on a web page.
Many types of Banner Ads exist such as: animated GIF, Flash or Static (JPEG).
Read more: How can I ensure that my banners reach their full potential?
Bid
Bid price is the price that a dealer or other prospective buyer is prepared to pay. In other words, Media buyers and advertisers alike, determine the maximum amount that he or she is willing to pay for certain traffic.
When it comes down to web marketing, there are a few places where you get the traffic with the highest bid price: Ad Networks, Google Adwords, etc.
Billing
Offer billing in affiliate marketing refers to a business model used by the advertiser to send online invoices to their clients for the products or services they offer.
Payment types can be one time or recurring. Most of the time with adult offers, end users are billed on a monthly basis (recurring) which allows you to gain more revenue through RevShare. This is also why you can make money from one single customer even years after the initial sale if he or she continues to spend.
Learn more about offer billing here: Billing misunderstandings by affiliates
Black Hat SEO
Black Hat SEO stands for search engine optimization practices that are considered “dirty” or “illegitimate”.
Even if these methods are sometimes effective at driving traffic, webmasters using Black Hat techniques run the risk of getting penalized by search engines by violating their terms of service.
Learn more about SEO White hat & black hat methods here:
Blacklist
If you possess a RON but decide to cease purchasing traffic from certain websites, establish a filter, commonly known as a Black List (BL). The term "Blacklist" can be utilized in various situations to avoid specific parameters.
Browser
A Browser is an application program used to interact and view information available on the World Wide Web.
Here are some of the most popular browsers freely available for download:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari (Mac)
- Internet Explorer
Campaign
The connection between an affiliate or source and the offer they're directing traffic to. A campaign is a more detailed version of an offer.
Capping
The maximum number of leads or sales - often predetermined - that an affiliate is allowed to generate in his or her affiliate account. Most new affiliates will experience a common lead cap on a popular offer or two!
Chargeback
Chargebacks are essentially refunds. It’s the term used to describe the reversal of funds when a consumer complains to their banking establishment over a specific charge / transaction on his or her credit or debit card.
The main idea behind chargebacks is to protect the cardholder at all costs from fraudsters and any other kind of unauthorized payments or theft.
It goes a little like this:
The consumer files a complaint with their bank over a specific charge, the issuing bank then investigates the validity of the claim; if the bank feels the complaint is valid and legit, the financial institution will then take the money directly from the merchant’s account and give it back to the consumer.
So, what’s the main difference between a chargeback and a refund?
The main difference is that the merchant has absolutely no say in the refund process that occurs during a chargeback.
Read More:
The Principles of Chargeback Prevention
Click Pixel
A JavaScript or image tag is inserted in an HTML landing page to track clicks when a redirect link is impractical.
Click Fraud
Creating fake clicks within a program utilizing the PPC price model. These clicks may stem from robots or humans. Given their useless traffic, individuals orchestrating click fraud are typically banned from affiliate networks.
Click ID
The user's identification code is a comprehensive set of information encompassing details about the segment, browser, hour, day, and more.
Cloaking
Cloaking is a Black Hat SEO technique in which the content visible to the search robots is different from to content seen by the user.
Co-branding
Also known as brand partnership, Co-branding is a situation where affiliates can add their own logo and branding to an existing product or service from the advertiser.
Commission
A commission is the amount of money earned by the affiliate after generating a sale, click-through or lead for the advertiser.
Commission rates are usually defined in the affiliate agreement.
Contextual Advertising
Contextual Advertising
Contextual advertising is a form of targeted advertising based on the content of the content of the page on which it is displayed.
For example, if the content of the page refers to ebony models, a contextual ad would display an ebony model as well.
Contextual Links
These are links found within a paragraph where a related idea is found.
Content Farm
The term used to characterize a website or a collection of websites that publishes substantial volumes of inexpensive, poor-quality content. This content is created to attract traffic from search engines.
Conversion Rate
One term you will often hear in the online marketing world is Conversion Rate or CR.
It’s defined as the percentage of users who accomplish a desired action (ex: click) on a webpage, generating a commission in the form of a lead or a sale in regards to the total volume of traffic who visited the page.
Cookie
Cookies are messages sent to the browser by a web server and stored in a text file on the visitor’s computer.
Recorded data in cookies can then be used by merchants to optimize their websites according to the user’s preferences. Cookies are usually stored 30 days in a user’s browser, or less, if cookies are manually cleared by the user before.
For affiliates, cookies are invaluable since they are used to track where the visitor came from (geo/device) and how much time elapsed between the first visit and the click-through/lead/sale.
CPA / RPA
CPA stands for Cost Per Action (also sometimes referred to as Cost Per Acquisition).
RPA stands for Revenue Per Action.
As you might have guessed, this is the backbone of the CPA-based advertising model, where the advertiser determines how much every conversion is worth. In this case, a conversion can be a click, a lead, a sale, and so on…
For instance, let’s say that your ad was clicked 500 times and that you were paid $1 for each click (Don’t get too excited, this example isn’t very realistic in the real world!).
In this example, the provider is reporting that you made $500 in new revenue. The CPA is calculated by dividing this number by the number of conversions (“sales” for example) generated.

CPC
CPC is an acronym for Cost-per-click.
Cost-per-click — also known as Pay-per-click — is an advertising model where an amount is paid anytime a user clicks on an ad.
CPI
CPI is an acronym for Cost-per-install.
Cost-per-install — also known as Pay-per-install — is an advertising model where an amount is paid anytime a user installs an application.
CPM / RPM
CPM stands for Cost per thousand (Mille) impressions.
RPM stands for Revenue per thousand (Mille) impressions.
In other words, CPM is the price you’d pay each time your ad has been seen 1,000 times.
Crawlers
Web crawling is a set of website URLs, referred to as seeds, that require visiting. The search engine's crawler explores each web page, recognizing all hyperlinks within the page and includes them in the list of locations to be crawled.
Cost per Sale – CPS
An online advertising payment model used after the acquisition of a product or service. The advertiser pays a pre-arranged fee once a potential client completes a purchase. CPS is predominantly employed during the phase when an actual transaction occurs, and a fee is subsequently paid to the publisher.
Cost per View – CPV
A billing approach for video advertisements determined by the quantity of views or interactions garnered by the ad.
Creative
Creatives are a synonym of advertising material or ad tools.
CTR
CTR stands for Click-through-rate.
Uttered in a percentage, a click-through-rate refers to the number of clicks related to the number of impressions. For example, let’s say that 2 people clicked on your banner out of 100 impressions — this would mean that your banner has a CTR of 2%.
Knowing something’s CTR is a way of measuring the success of a campaign.

Deep linking
In search engine optimization, deep linking refers to internal links or backlinks that are structured deeper within your site's network of other links. In other words, a page that isn’t the homepage.
Demand-Side Platforms (DSP)
Platforms where digital advertising inventory can be purchased, offering access to various ad exchanges. This allows users to acquire traffic from a diverse array of sources.
Datafeed
A document that includes a catalog of products offered by a specific advertiser, typically featuring details such as descriptions, images, and prices of the promoted items.
Dayparting
Lets you focus on particular days and hours based on their performance. Analyze your statistics for a few weeks on an hourly basis and identify optimal time periods or hours to target.
Direct Linking / Direct to Form
Direct linking is the process where an affiliate links directly to the merchant or advertiser without going through a landing page or pre-sale page.
In other words, Direct linking gets you straight to the product or offer so customers don’t have to jump through hoops before being shown the relevant page.
Direct Billing Flow
When the billing is conducted directly through the identification of the mobile phone's MSISDN, charges are deducted from the cell phone's balance.
Direct Buy
This involves acquiring traffic in large quantities through direct communication with website owners. Such transactions typically yield both high and low-quality traffic. Direct buy arrangements are known for their transparency, providing detailed information on your position, impressions, expenditures and dates. However, the drawback lies in the lack of targeted optimizations since the entire traffic stream is received. Some ad networks also offer this option, eliminating the need to contact the website owner directly.
Disclosure
A notification or webpage on your site that guarantees your visitors are fully informed about the fact that you receive compensation for any purchasing recommendations or service endorsements featured on your site. Such a disclosure is essential for compliance with FTC laws.
Domain
A domain name is the main name used in your website address.
A domain name is usually related to a brand and/or a specific keyword.
For example: www.DomainName.com
Read these articles for more information on how to choose domain name(s):
Domain Authority
A rating, measured on a 100-point scale, developed by Moz to forecast the anticipated ranking performance of a website across all search engines.
Double Opt-In (DOI)
A double opt-in refers to a signup process where the user has to confirm his email address to confirm his subscription.
The double opt-in is mostly used for email marketing campaigns where users are invited to subscribe to mailing list. However, the double opt-in can also be part of other type of signup processes.
Dynamic Tracking
An essential tool that lets you monitor both your actions and investments. Typically, ad networks and DSPs offer numerous tracking tokens for you to integrate into your offer links, maximizing the collection of relevant data
eCPM
eCPM stands for Effective Cost Per thousand (Mille) impressions.
It’s used to determine your earnings per thousand impressions. First, you need to divide your earnings by your number of impressions. Then, you multiply this number by 1000 to bring it back to your eCPM.

For an example of eCPM calculation, please see:
All About Media Buying – Part 3 – Profit Calculation
EPC
EPC stands for Earnings Per Click.
EPC is an important metric used to measure performance. The EPC for an offer can be determined using a very simplistic calculation:
Your Earnings Per Click (EPC) is your earnings divided by the number of clicks your ad received.
Be careful, though! Many networks have been known to display EPC information in a misleading manner since they provide the amount generated for 100 clicks instead of just one.
This method of display and reporting can artificially inflate the affiliate’s EPC while, in reality, the affiliate may be earning less. That is why it is crucial to take into account additional metrics other than simply relying on an offer’s EPC to assess the quality of an offer.
Read more here:
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT EPC
Ecommerce
The act of purchasing and selling tangible goods on the internet, such as on platforms like eBay, Shopify, WooCommerce, and various other online marketplaces.
First Click
The First Click – also called a first interaction model – is a model that assigns full credit for a conversion to either the initial user or the first marketing channel, with no specified limit on cookie expiration.
Flat rate
Flat rate buys are purchases that are fixed in price. For example, a flat rate traffic buy means that the price won’t change regardless of how much – or how little traffic you receive.
Flat rate buys are typically reserved for the biggest media buyers out there.
Many great ad spots that provide high volumes of traffic sell at a fixed monthly price.
But remember, when dealing with flat rates, you need to pay the right price, and that requires a very accurate evaluation so you know what you’re getting.
Flat Deal
This involves purchasing traffic in large quantities through direct communication with website owners or by negotiating with an ad network. Such transactions typically return both high and low-quality traffic. Direct buy arrangements are known for their high level of transparency, providing detailed information on your position, impressions, expenditures, and dates. However, targeted optimizations are not feasible as you receive the entire traffic stream. Some ad networks also offer this option, eliminating the need to contact the website owner directly.
Frequency Capping
The frequency represents the count of times (impressions) a singular user encounters each ad within a specified time frame.
Geo-targeting
Geo-targeting is tailored, targeted advertising geared towards, or based upon, the geographic location of your visitors. It’s displaying certain ads or offers based on the country your visitor is from.
Global Postbacks
Where single postbacks allow affiliates to track a single offer, Global Postbacks allow affiliates to track all offers with a single URL.
It is considered to be the most accurate and reliable tracking tool. One of its many advantages is how much of a time-saver it can be as it allows the tracking of multiple offers without hassle.
You can learn more about Global Postbacks here: What are Global Postbacks?
Gross Click
Unlike unique clicks, Gross clicks are the number of clicks in total…in other words all the clicks that were made by the user. For example, if the same user clicks 5 times on the same offer/banner, it will show 5 gross clicks. Using gross clicks for your calculation will tend to dilute the EPC value.
Impression
Impression is an important term to keep in mind when toying with online advertising. This is how many times ads are displayed or viewed on a website.
Impressions – also called views – are recorded each time a specific ad is shown to the viewer.
In-house
When you do something in-house, you call the shots and don’t need any outside help.
Instead of using an affiliate solution provider or resorting to outsourcing, in-house refers to the creation and management of your very own affiliate program.
This can be done by acquiring a third party product or starting a new program from scratch.
Internal Linking
A hyperlink pointing to the same domain as the one hosting the link. An internal link leads to another page within the same website.
Inbound Link or Backlink
A link originating from a website external to your own.
Incentivized Affiliates
A scenario where website visitors are provided with incentives to fulfill a specific action, leading to the affiliate earning a commission. The incentives can take various forms, ranging from prizes and discounts to monetary rewards or even free subscriptions.
Index
It refers to the database employed by a particular search engine containing information about all the sites the search engine can discover. If a website is not present in the search engine's index, users won't be able to locate it using that specific search engine.
Landing page
A Landing page is basically a sales page.
The Landing page is particularly important because the role of the page is to sell or convince the visitor to do something (aka generate a conversion).
In CPA terms, we want this page to convince the user to perform a certain action.
Read more here:
- LANDING PAGES 101
- LANDING PAGES 101 – PART 2
- LANDING PAGES 101 – PART 3
- 3 TIPS TO CREATE BETTER LANDING PAGES
- HOW TO MAKE A DEDICATED LANDING & AVOID THE CRASH – PART 1
- HOW TO MAKE A DEDICATED LANDING & AVOID THE CRASH – PART 2
Lead Scrubbing
Lead scrubbing is the term attributed to the process of removing non-legitimate leads.
So, what generally constitutes a non-legitimate lead?
- “bogus” entries (e.g., fake email submissions, “Asdf@Asdf.Com“, etc.)
- inaccurate or falsified info
- duplicate submissions (based on IP address)
- fraudulent activity
- leads generated through Spam and other Terms of Service infringing techniques
Learn more about lead scrubbing with this article: LEAD SCRUBBING — What It Really Means
Link Juice
This term is part of SEO and represents the equity or influence transferred to a website through links from internal or external sources. This influence is akin to a vote or recommendation for a website. It stands as one of the most vital factors in determining your website's Search Engine Results Page (SERP) ranking and PageRank.
Loyalty Affiliates
Similar to incentivized affiliates. However, the reward structure for traffic differs. Specifically, the reward entails a more extended commitment to the merchant. Users are expected to become full site members, engaging in activities and making purchases.
LSI Keyword
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are words that bear semantic relevance to your primary keyword, such as synonyms or acronyms.
Media Buying
The act of media buying relates to the purchase of traffic for advertising purposes.
In other words, the affiliate media buyer’s #1 goal is to find ad space to negotiate a deal on, purchase, and then monetize by reaching the most number of people, at the lowest possible cost.
Head out to the media buy section of our Blog if you want to become a successful media buyer.
Merchant
Merchant is just another name used for advertiser.
In a business relationship, the merchant pays affiliates after the’ve sent traffic towards specific offers or products in order to generate a desired action (lead/sale/etc.).
Multi-CPA
The Multi-CPA label is used to indicate when an offer may consist of different payout types.
For example, when you use CrakRevenue Smartlinks or promote a CrakRevenue Survey, the offers shown to the user will vary depending on their geographic location and the device he or she is using. Therefore, the conversion model may vary as well and – consequently – the payout type.
Therefore, a multiple-payout model usually consists of a mix of Pay Per Lead (DOI & SOI), Pay Per Sale, and Revshare & Lifetime Revshare payouts.
Multiple Tiers
If you ever hear the term Multiple Tiers, it means a business model where affiliates can earn additional commissions from sales generated by other affiliates under them.
Niche
A niche can be thought of as a highly-specialized market.
Here are some examples of niches in adult affiliate marketing:
Amateur, MILF, BBW, Emo, Hentai … we think you can take it from there.
Offer
In affiliate marketing, an offer usually refers to the affiliate offers. In other words: the affiliate offer or program run by an advertiser or a CPA Network.
Indeed, we usually refer to the product or service promoted through the affiliate offer by product which is destined to the end-users (traffic that buys the product).
Optimization
Refining an existing marketing campaign through adjustments to improve its overall performance and outcomes.
Opt In Email
A solicited email, requested by the recipient.
Payout
The earnings accumulated for each sale or conversion. Affiliates receive monthly payouts based on the sales generated by referred users.
PageRank
Google employs PageRank, an algorithm that determines the ranking of websites in its searches. It assesses a page's significance by analyzing the quantity and quality of inbound links. Although not the sole algorithm used by Google to evaluate web pages, it stands out as the most widely recognized.
Placement
The website where your landing pages or banners are displayed.
Pay Bump
When an affiliate earns an increased payout for a particular offer.
Pay-Per-Lead (PPL)
Pay-Per-Lead or PPL refers to a commission model where affiliates get paid once they deliver a lead to the advertiser.
In internet marketing, the term lead refers to a prospective client.
Leads usually take the form of a valid email address subscription delivered on a SOI or a DOI model.
You can learn more about PPL here: A Crash Course Guide to Pay-Per-Lead PPL
Pay-Per-Sale (PPS)
Pay-Per-Sale or PPS – also known as Cost-Per-Sale (CPS) – stands for Pay Per Sale.
It refers to a pricing model where affiliates are paid once they directly generate a sale from the merchant’s or advertiser’s website.
A PPS offer typically pays more per individual sale, but it often has a lower associated conversion rate than its PPL (pay-per-lead) counterpart. This is because PPS offers require the user to enter their credit card information to classify as a sale.
In most cases, assuming the user enters their credit card information, the affiliate will still earn the PPS commission even on trials.
Payment Threshold
The minimum threshold of earned commissions required for withdrawing funds in affiliate marketing.
Performance-Based Marketing
Performance-Based Marketing is a method of interactive advertising in which the merchant or advertiser pays affiliates only when a measurable action is completed – such as a click, a sale or a lead.
With the popularity of online advertising, Performance-Based Marketing is more relevant (and spread out) than ever before. Here are some of the many advantages merchants and advertisers are relying on.
Performance-Based Marketing:
- Cost-effective advertisements (especially neat for tight budgets)
- You only pay for results
- Better targeting as the merchant or advertiser assumes all the risks
Postback
A postback is like a trigger set on the offer that sends a message back to the server as soon as an action – usually a conversion – is made. Therefore, you can set postbacks to receive information to your own statistic tool.
If you only wish to check your Stats with us from your CrakRevenue affiliate panel, you do not need a postback.
Read more here:
PPC / RPC
PPC stands for Pay Per Click.
RPC stands for Revenue Per Click.
If you were promoting a PPC offer, Pay Per Click means that you would get paid each time a user clicks on your ad or sponsored link. It’s by far the fastest way to earn money! However, the amount you would typically earn per click is comparatively low when compared to CPA payouts.
Prelander
Prelanders are sales pages designed to provide a few key details about specific offers to spike interest and prequalify traffic.
For example: a pre-lander sales page might contain some short text and a "Read More" call-to-action (CTA) button which then prequalifies your traffic based on their continued interest and takes them to the offer’s final landing page.

Publisher
Simply a different term for "affiliate."
Revshare, RPS, and RS
Revshare — sometimes labeled as RS or RPS — stands for Revenue Sharing.
At CrakRevenue there are 2 types of Revshare programs:
1) Revshare Lifetime
When you promote a Revshare lifetime offer, it means you get a percentage of whatever your user spends — anytime your user spends anything.
Revshare Lifetime income is for the lifetime of the user you refer and it never expires.
Example: If you are promoting a Lifetime Revshare Cam offer, and the user registers for free, you receive no commission for this lead. You would only receive a commission if this lead of yours eventually decided on upgrading their account and purchases “tokens” or “credits.” If the token or credit package costs $19.99, you would receive X% of that number, and this would be your Revshare earnings on that particular amount.
2) Revshare
When you promote any Revshare offer, it means you receive a promised percentage of the commissions paid by your traffic, from the advertiser.
This means that the commission paid is shared by CrakRevenue and its affiliates.
Example: If you are promoting a Revshare Nutra offer, and your user purchases a bunch of products, you receive a percentage of the commission paid by the advertiser: The commissions are shared between CrakRevenue and you. If your user spendings are $100 for instance, and the payout offered is set at 80% Revshare, you’ll receive $80 by of the payout.
For examples on how profitable Revshare offers can become, please see:
ROI
ROI stands for Return on Investment.
This is essentially the money you earned minus the money you’ve spent. In other words, your gross profit.
RON
A RON is a package usually offered by Ad Networks that will include many sources of traffic. Your ads will rotate on a network of sites. Some great, some rubbish.
Advantage: it gives you a better price than what you would have typically paid for their best source of traffic.
Disadvantage: you will need to optimize your network after your first test, to discard bad sources of traffic.
RTB: Real-time bidding
It's a technique where bids are placed for each impression in real-time auctions during the loading of a web page, contrasting with static bidding, where bids are made in batches of up to several thousand impressions.
Search Robots
Also called Search Engines Spiders or Web Crawlers, Search Robots are bots used by search engines to crawl your website in order to index its content.
Allowing search robots to crawl your website will lead to seeing your website listed in SERP.
Segment
Segments are comprised of a specific group of users who are sharing the same feature(s) within your entire traffic, leads or clients for example.
Segments are used to split large volume of individuals into smaller groups in order to optimize targeted marketing.
SEO
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. In web marketing, SEO is used to optimize websites in order to make them more visible through search engines such as Google for example.
By helping their website rank higher in SERP, SEO techniques help webmasters generate organic / natural traffic which is a free source of qualified traffic.
SERP
SERP stands for Search Engines Results Pages. This is the page where websites are listed when a web users type a request on a search engine search bar such as in Google.
Single Opt-in (SOI)
Single opt-in refers to a signup process where the user doesn’t have to confirm his email address to confirm his subscription.
In other words, it’s a sign-up process where a web user just enters his email to access a page, a program or to subscribe to a mailing list for example.
Smartlink
Smartlinks sends your traffic to CrakRevenue’s top-converting offers based on user device, user location and your chosen vertical.
Smartlinks helps you get more conversions by generating links to only creatives & landers that have proven to have the highest CTR head and shoulders above the rest.
Spot
Mainly used by media buyers, the term spot refers to an advertising placement on a website page.
Targeting
Targeted Marketing aims to identify the best audience for a specific product or service. The goal is to show advertisements tailored to the needs and interests of people who are already interested by what you’ll be offering them.
Using targeted marketing has many advantages, especially for businesses with specialized products or services. Since you will be advertising products or services that matter a lot to users, they will be more likely to spend money.
Here are some key elements that distinguish targeted marketing from other strategies:
- It’s much more focused and segmented
- The ability to pinpoint a very specific group by geo/age/salary/etc is great
- It’s more productive than broader marketing strategies
Tracker (Sub ID)
A tracker (Sub ID) is a way to tag your campaigns, traffic sources, ad spots, and banner names. A tracker helps you pinpoint how many hits are coming from a particular source and how many sales are being generated.
Trackers are data… and data is information.
The information contained within a tracker should be relevant to your campaigns. Trackers can be thought of as little memory cues that can help jog your memory on what you’ve done (that turned out to be successful), or that provide you with great insight of your success.
Read more here:
- TRACKERS: THE SILENT HEROES OF EVERY CAMPAIGN
- Be on the Right Track Part 2 – Analyzing Your Trackers
- BE ON THE RIGHT TRACK PART 3 – EFFICIENT TRACKERS
Text Link
A hyperlink to an advertiser's website without an accompanying image.
Token
A tracking token is a dynamically generated variable offered by a paid traffic network. These tokens, embedded in offers' URLs, serve to track specific information in an ad campaign. Typically, multiple tokens can be added to your tracking software to aid in optimizing your campaigns.
Top-level domain (TLD)
The concluding section of a domain name, typically following the final dot in a web address, is referred to as the "TLD" letters.
Unique clicks
A unique click is a click associated with a single Internet Protocol (IP) address or computer.
This means that no matter how many times a user clicks on your ads, it will only be registered once as a unique click. This is especially important to prevent fraudulent activity.
For obvious reasons, unique clicks are much more valuable than gross clicks or hits.
Vertical
Verticals refers to markets targeting a specific audience. For example, Online Dating is a vertical one might say is targeted towards single people looking for love online.
White Hat SEO
In contrast with Black Hat SEO methods, White Hat SEO refers to all techniques and strategies generally deemed fair and acceptable by most search engines.
Learn more about SEO and all the Different Shades of Grey here!
White Label
White labels are your best shot at getting that shiny product or service without spending weeks if not months in development — and all the related costs. They are existing websites, products or services rebranded with another name.
In other words, white labels allow you to run your own branded “clone” of a website or a program.
Learn more about white labels here: What are white labels?



